Case ID:
HJF 562-20
Web Published:
1/23/2023
Currently, anti-retroviral therapy (ART) based on controlling viral replication is the most effective treatment for HIV. However, HIV drug resistance can compromise the effectiveness of ART.
Researchers at Uniformed Services University of Health Sciences (USU) and Henry M Jackson Foundation (HJF) in collaboration with scientists at Université de Montréal and Centre de Recherche du CHUM (CRCHUM) have developed novel human CD4 (Ab-CD4) or CD4 mimetic compound (CD4mc) antibody conjugates that neutralize and kill HIV-infected cells.
Applications and Advantages
- A novel antibody therapeutic that neutralizes and kills HIV infected cells unlike ART that only suppresses viral activity
- Therapeutic applications include parenteral administration of an effective AB-CD4 pharmaceutical composition to a HIV patient.
- Potential access to uncrowded market space as currently only one FDA approved antibody treatment exists for HIV
Innovation Description
ART treats HIV by suppressing the virus’ activity in the body. ART-treated individuals still experience several co-morbidities, including increased cardiovascular disease, bone disorders and cognitive impairment. Additionally, therapy interruption leads to the re-emergence of viral replication and AIDS progression. Currently, the need for a curative therapy remains unaddressed.
Our researchers have developed new CD4 and CD4 mimetic conjugated antibodies (Ab-CD4/CD4mc) that effectively “open” “closed” regions of the HIV cell envelopes (Env). With this opening, antibodies that were non-neutralizing (nnAbs) because of lack of binding targets in the closed conformation, now act as potential mediators of Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC)
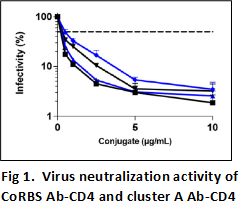
and/or Antibody-Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis (ADCP) killing of HIV-infected cells. As the Env sites recognized by the nnAbs map to highly conserved regions of the Env, their potential utility as targets for protective antibody therapeutics is deemed high once they are made accessible by these new conjugates. Functional studies fully validated the Ab-CD4 hybrid proteins’ (with either CoRBS or Cluster A Ab arms) effective recognition and killing of VSC-G-pseudotyped HIV-1 JRFL infected cells. Fig 1. shows decrease in infectivity due to virus neutralization by Ab-CD4 clusters (dashed line represents 50 % infectivity).
Inventors
- Marzena Pazgier, Ph.D., USU
- William D. Tolbert, Ph.D., USU
- Dung N. Nguyen, Ph.D., HJF
- Andrés Finzi, Ph.D., Université de Montréal
- Jonathan Richard, Ph.D., CRCHUM
Innovation Status
Virus recognition and killing of infected cells by the Ab-CD4 hybrid proteins has been validated in vitro. Efforts are on-going to optimize antibody production and, to evaluate the ability of conjugates to reduce the size of the latent HIV reservoir, ex-vivo. Please see mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5).
Intellectual Property Status
A PCT application has been filed (PCT/US22/32958).