Case ID:
HJF 485-17
Web Published:
1/19/2023
A technology for screening and diagnosing prostate cancer based on urine exosomes is available for licensing from HJF.
Applications and Advantages
- Screening for and diagnosis prostate cancer with superior accuracy than the standard of care.
- Convenience of using regular urine sample that can be collected at home, as opposed to post-DRE urine sample.
- RNA molecules in exosomes are protected from degradation.
Innovation Description
In clinical practice, early detection of prostate cancer is performed by serum prostate specific antigen (PSA) testing and digital rectal examination (DRE). Serum PSA has remarkably increased prostate cancer detection, but the test exhibits low specificity and low positive predictive value resulting in high negative biopsy rate and overtreatment. Elevated PSA levels can be detected in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostatitis with no malignancy.
To overcome this challenge, scientists from HJF and the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USU) have developed a novel method for screening for and diagnosing prostate cancer by measuring transcript levels of two genes in exosomes isolated from regular urine. Validated using an independent cohort of patient samples collected in a prospective setting, this assay exhibits a significant superior performance than the standard of care (SOC) method which consists of patient’s serum PSA level, age, and race. This technology would benefit both prostate cancer patients of both Caucasian and African descent from avoiding unnecessary biopsy. Furthermore, the use of regular urine sample that can be collected at home as opposed to post-DRE urine that has to be collected in a doctor’s office, offers an added convenience and more acceptability to patients. Unlike existing technology that measures transcripts in cell-containing urine, the present technology measures transcripts in urine exosomes that protect RNA molecules from degradation thus further providing convenience in sample storage and transportation.
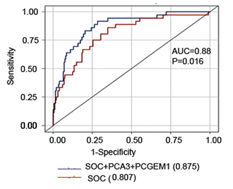
Figure 1. Urine exosomal 2-gene panel (PCA3, PCGEM1) in combination with SOC predicts high grade prostate cancer at diagnostic biopsy. AUC for performance of gene marker panel (PCA3, PCGEM1) plus SOC for predicting high grade cancer at biopsy.
Inventors
- Indu Kohaar, Ph.D. HJF/USU
- Gyorgy Petrovics, Ph.D. HJF/USU
- Shiv Srivastava, Ph.D. USU
Innovation Status
Methods have been developed and validated using an independent patient cohort in a prospective setting. Please see: The Journal of Urology 2021; 205(2):420-425 .
Intellectual Property Status
Patent applications have been filed in the U.S. (16/611,692), Europe (18798896.9), Canada (3,062,573), and Australia (2018266632).